Architects hold a crucial role in designing structures that cater to the needs of clients while also contributing towards the betterment of the environment.
With the world's pressing issue of water scarcity, it’s vital to explore methods in which we can conserve this valuable resource. Thankfully, Vectorworks design software contains a range of features that aid in reaching this goal.
In this article, you’ll read about three Vectorworks features you can put to work to design for water conservation in your projects.
FEATURE #1 – Content Libraries
One way you can have an impact on the environment is by selecting water-efficient plumbing fixtures and systems to go into the building. With Vectorworks, you can find tons of symbol resources within the Resource Manager such as toilets, showerheads, faucets, dishwashers, and washing machines.
The Resource Manager contains plenty of eco-friendly appliances that you can easily insert into your projects. But how do you include and document important information such as water consumption for these fixtures?
Custom records can be attached to your symbols to accurately report that information.
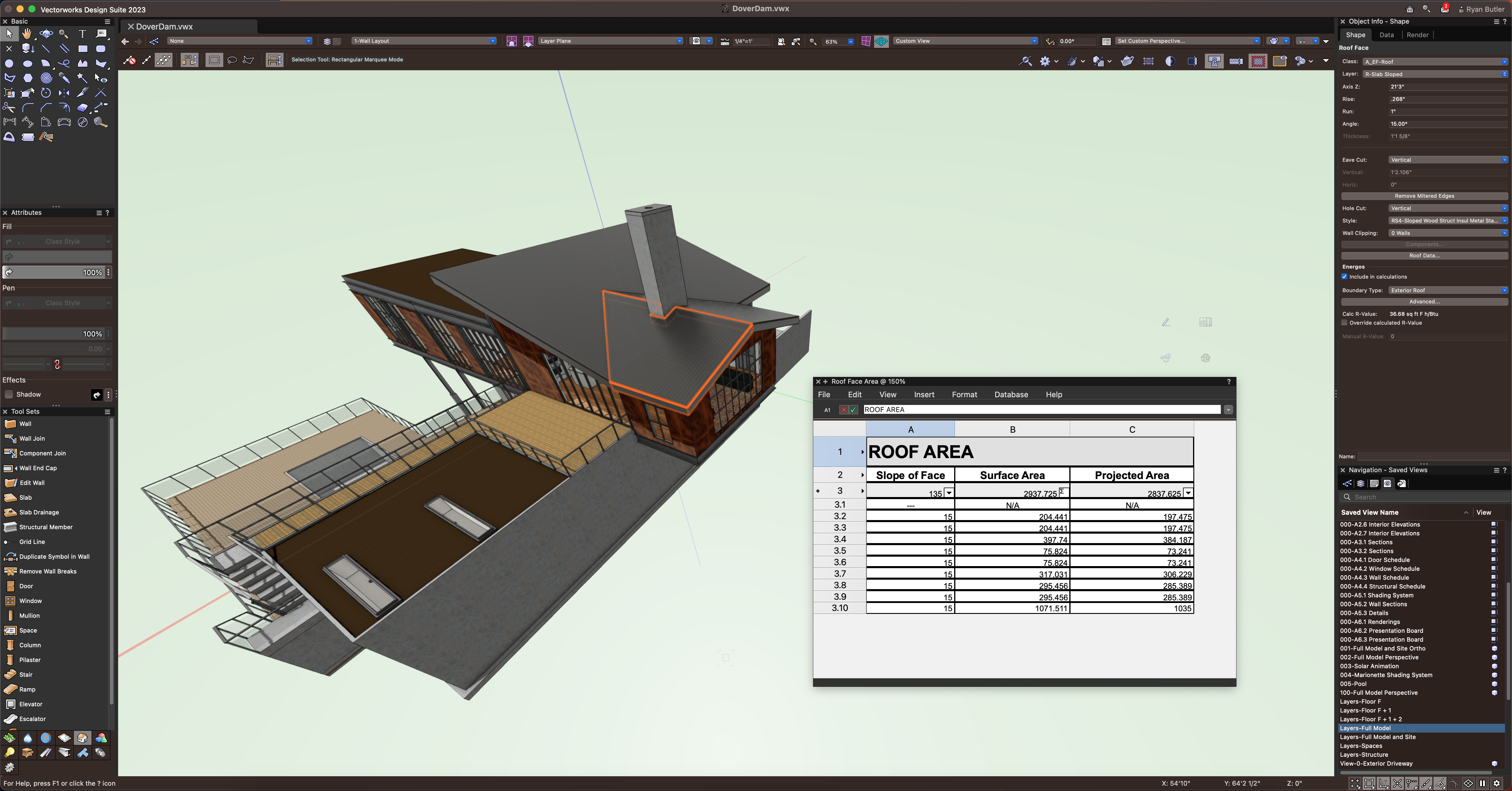
FEATURE #2 – WORKSHEETS
If you're designing to meet specific goals for a sustainable or green building, reporting project data is crucial. To do this accurately, take advantage of worksheets in Vectorworks.
With worksheets, you can calculate the total water use of the building by quantifying the number of plumbing fixtures and multiplying by the water-use values determined by the custom record of each fixture.
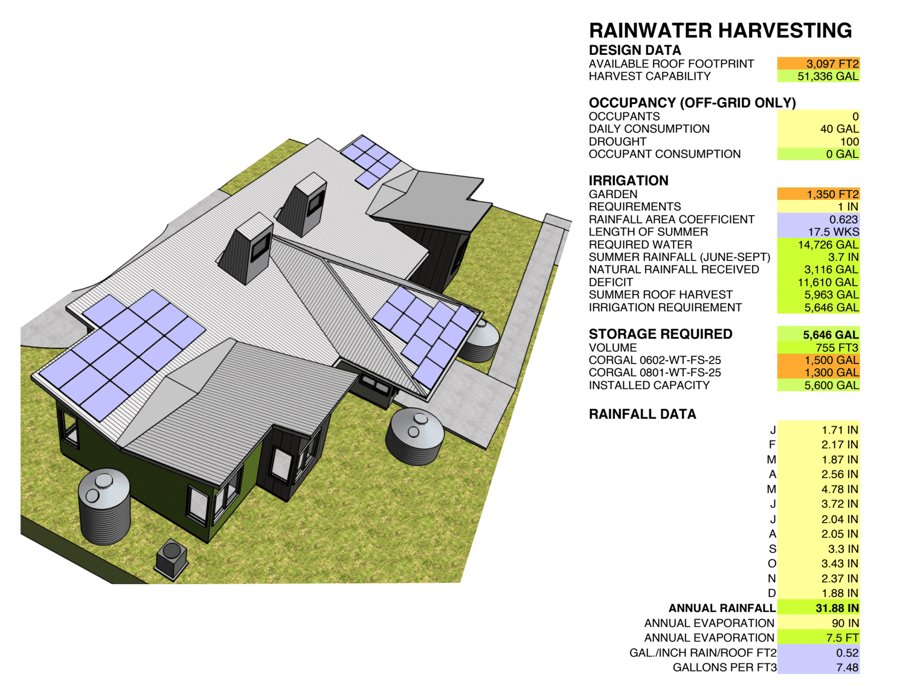
One way you can use worksheets is to report on roof area and annual/monthly rainfall. This prepares you to design more effective water harvesting systems. François Lévy used this method to determine the necessary sizes for water-catching basins in his webinar, “Sustainable Resources for Small-Scale BIM.”
If you’re looking for ways to work better with data in Vectorworks, our post, “3 Ways to Maximize Your Data Use for BIM,” has you covered.
FEATURE #3 – SITE MODELING
One of the most impactful design strategies for water conservation is related to the project’s site. We’ve already mentioned harvesting rainwater, and there’s a lot more you can do regarding the site, especially using Vectorworks’ site modeling tools.
You can find more information about sustainable site design in this blog post.
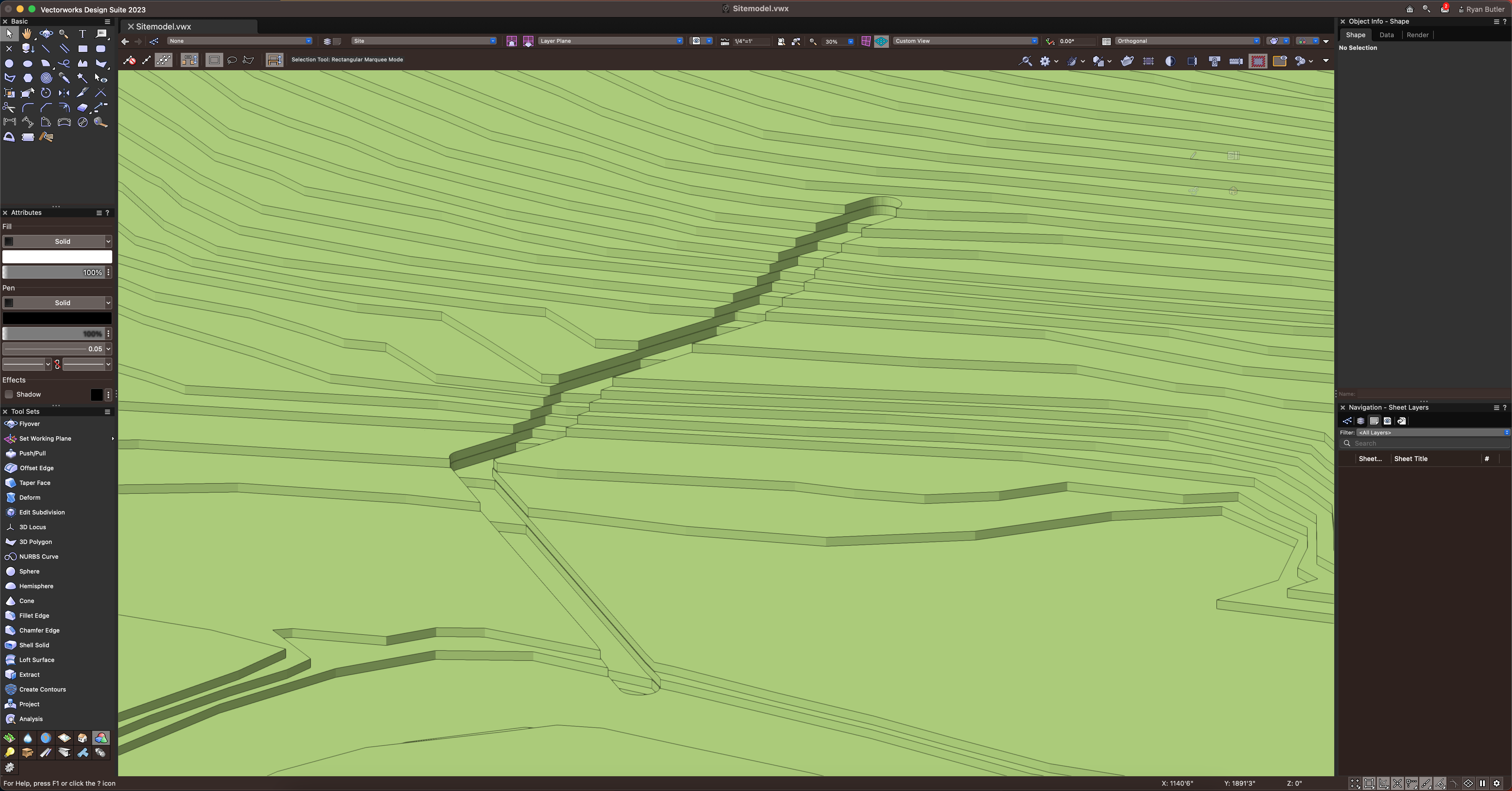
By modeling the site to mitigate water runoff, you can make the site more water efficient. You can do this by using bioswales, berms, and other methods explored in our free course, “Integrating Design Technology for Water-Efficient Landscapes.”
BONUS TIP – OPTIMIZING BUILDING ORIENTATION
We just couldn’t conclude this post without mentioning building orientation. It’s not quite a Vectorworks feature all on its own, but it’s a topic worth mentioning.
A building’s position on the site can play a big role in its water efficiency. Optimizing the building’s orientation reduces the necessary size of heating and cooling systems, which will reduce overall water consumption and, of course, energy consumption. You can use the Heliodon tool to create solar animations to accurately account for sun patterns in your design.
Looking for more tips about designing sustainable buildings with Vectorworks Architect? Meet your goals with early-phase energy modeling, which you can learn more about below.

.svg)